Unlocking Sound: Discover the Magic of Assistive Listening Devices for Enhanced Hearing!
In a world filled with sounds that enrich our daily lives, many individuals face challenges in experiencing these auditory experiences due to hearing loss. Assistive listening devices (ALDs) play a crucial role in bridging this gap, enabling individuals to engage more fully in conversations, educational settings, and social gatherings. As the demand for effective communication tools continues to grow, ALDs have emerged as essential companions for those with hearing impairments. They not only enhance sound but also transform lives, allowing users to connect with others and their environment in meaningful ways. This article will delve into the various types of ALDs, how they function, their myriad benefits, and tips for selecting the right device to ensure that no one is left behind in the conversation.
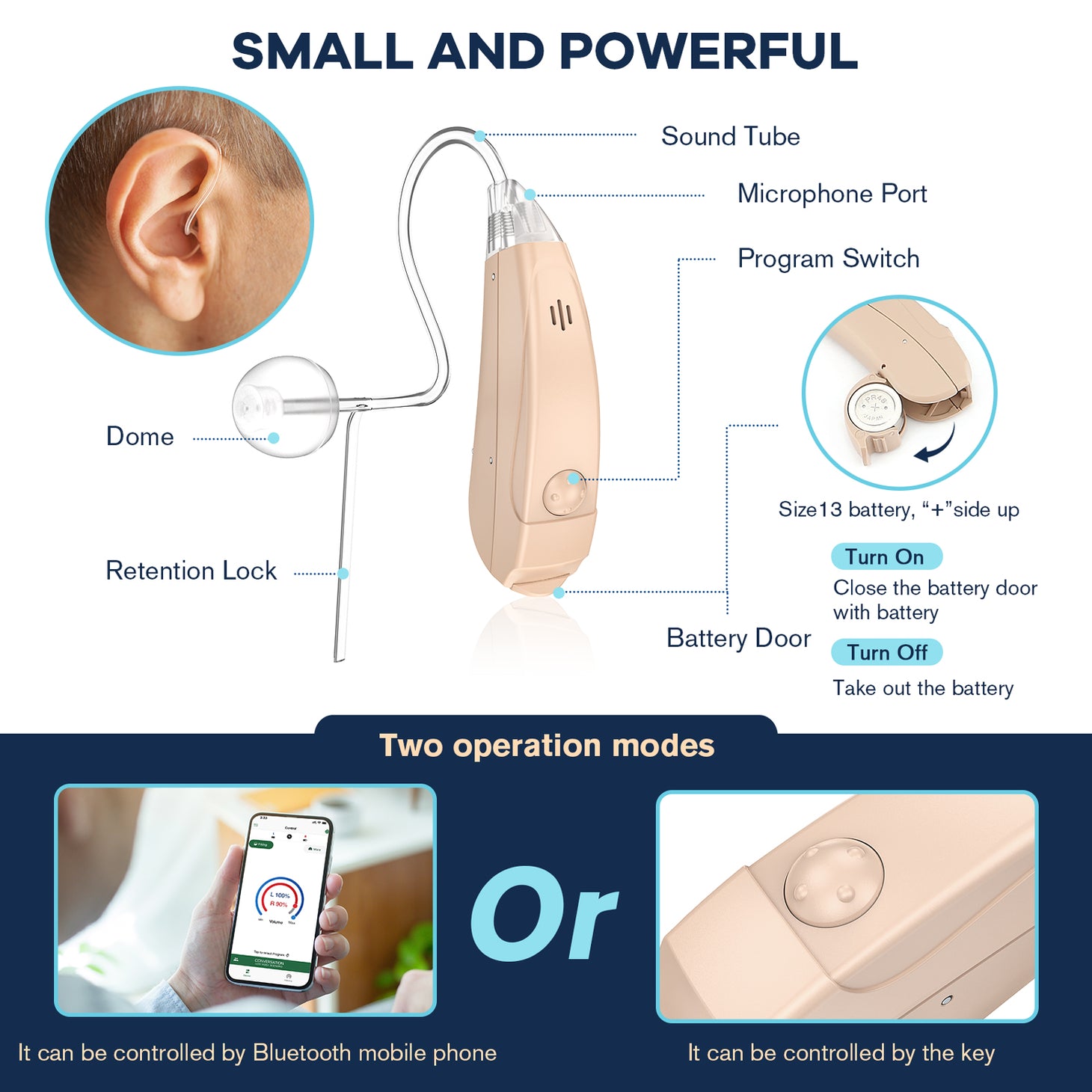
Understanding Assistive Listening Devices
Assistive listening devices are specialized tools designed to improve sound reception for individuals with hearing loss. Unlike traditional hearing aids that amplify all sounds, ALDs focus on enhancing specific sounds, making them particularly useful in environments where background noise can be distracting. There are several types of ALDs, including personal amplifiers, FM (frequency modulation) systems, and induction loop systems. Personal amplifiers are portable devices that users can hold or wear to amplify sounds in close proximity. FM systems, on the other hand, use radio waves to transmit sound from a microphone directly to a receiver worn by the listener, making them ideal for classrooms or conferences. Induction loop systems utilize electromagnetic fields to transmit sound directly to hearing aids equipped with telecoils, providing a seamless listening experience in public venues. Understanding these differences is vital for individuals seeking effective solutions to enhance their hearing.
How Assistive Listening Devices Work
The technology behind assistive listening devices is designed to capture sound clearly and transmit it to the user with minimal interference. Most ALDs consist of three main components: microphones, transmitters, and receivers. Microphones pick up sound from the environment, while transmitters send the sound signal, often using radio waves or infrared light, to the receiver. The receiver then converts this signal back into sound, which the user can hear through headphones or directly into their hearing aids. A significant advantage of ALDs is their ability to reduce background noise, enabling users to focus on the desired sound, such as a speaker in a crowded room. This clarity is particularly beneficial in educational contexts or social situations where multiple conversations may be taking place, allowing users to experience sound without the overwhelming distractions that often accompany it.
Benefits of Using Assistive Listening Devices
The benefits of ALDs extend far beyond improved sound quality. For individuals with hearing loss, these devices can dramatically enhance communication abilities, allowing them to participate more actively in conversations and social activities. Friends of mine have shared how ALDs have transformed their experiences in group settings, with one mentioning that using an FM system during a family gathering helped them engage more fully, rather than feeling isolated due to their hearing challenges. Additionally, ALDs can significantly improve learning experiences in educational environments, allowing students to absorb information more effectively during lectures or discussions. By reducing feelings of isolation and enhancing social interaction, assistive listening devices contribute positively to the overall quality of life for users. These devices empower individuals to reclaim their voice in conversations, fostering a sense of belonging and connection.
Choosing the Right Assistive Listening Device
Selecting the most suitable assistive listening device can seem overwhelming, given the variety of options available. It's essential to consider individual needs, the specific environments where the device will be used, and compatibility with existing hearing aids. For instance, someone who frequently attends lectures might benefit from an FM system, while a person looking for a personal amplifier for one-on-one conversations may find a handheld device more appropriate. Ease of use is another critical factor; devices should be user-friendly and comfortable to wear. Additionally, consulting with a hearing specialist can provide valuable insights into which device would best suit an individual's lifestyle and communication needs. Ultimately, the right ALD can make a significant difference in enabling users to hear and engage with the world around them.
Summary of Assistive Listening Devices
In summary, assistive listening devices are vital tools that enhance hearing and communication for individuals with hearing loss. By understanding the different types of ALDs and how they work, users can make informed decisions that improve their daily interactions and overall quality of life. As we continue to explore the potential of these devices, it becomes increasingly clear that they offer a pathway to overcoming hearing challenges. Whether in educational settings, social gatherings, or professional environments, ALDs can unlock the sounds of life, fostering connections and enriching experiences for those who use them. If you or someone you know is facing challenges with hearing, consider exploring the world of assistive listening devices as a viable solution for enhancing communication.



